2020 카카오 블라인드 채용 코딩 테스트 문제입니다.
코딩테스트 연습 - 외벽 점검
레스토랑을 운영하고 있는 "스카피"는 레스토랑 내부가 너무 낡아 친구들과 함께 직접 리모델링 하기로 했습니다. 레스토랑이 있는 곳은 스노우타운으로 매우 추운 지역이어서 내부 공사를 하
programmers.co.kr
문제 확인
2가지 풀이법이 있습니다.
- 비트로 수리한 외벽을 체크하고 완전 탐색
- 퍼뮤테이션을 통해 완전 탐색
풀이
1번 풀이의 경우
큐를 통해 bfs 완전 탐색을 하며 최대 15개의 점검해야 할 외벽이 있기 때문에 각 외벽을 2^i 비트로 표현합니다.
010100의 의미는 점검해야 할 외벽 6개 중에서 i : 2, 4에 해당하는 외벽을 점검 완료하였다는 의미를 가집니다.
현재 위치의 벽을 dist[i]로 설정하고 dist[i] 가 갈 수 있는 위치까지의 외벽을 모두 점검 표시하며 완전 탐색합니다.
2번 풀이의 경우 퍼뮤테이션 함수 next_permutation 함수로 dist 배열을 완전 탐색하면서 가능한 경우의 수를 모두 점검하고 수리할 외벽을 0 ~ n까지 순서대로 대입하면서 depth를 찾고 depth의 최솟값을 탐색합니다.
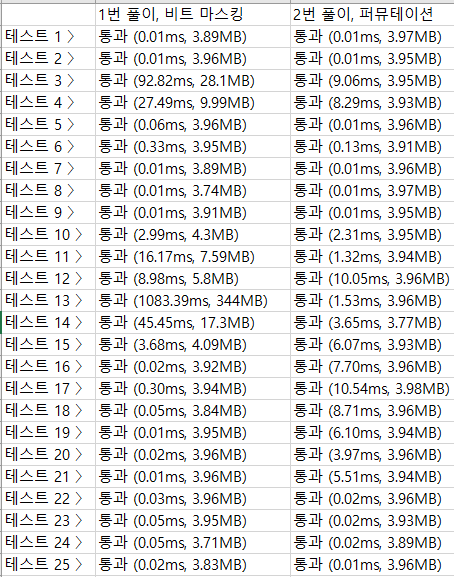
1번 풀이의 경우 큐를 활용해야 하며 완전 탐색을 해야 하기 때문에 큐 크기가 매우 커질 수 있으므로 시간, 메모리 모두 높습니다. 2번 풀이의 경우 기존의 dist 배열을 퍼뮤테이션 하며 추가로 배열을 사용하지 않기 때문에 메모리가 높지 않으며 큐의 push, pop에 의한 작업시간이 없으므로 더 빠른 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
코드
1. 비트 마스킹
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int solution(int n, vector<int> weak, vector<int> dist) {
int wn = weak.size(), dn = dist.size();
int n_bit = 1 << wn;
sort(dist.begin(), dist.end(), [](int a, int b)->bool {
return a > b;
});
int depth = 0;
queue<int> que;
que.push(0);
while (!que.empty() && depth < dn) {
int cur_size = que.size();
while (cur_size--) {//현재 depth의 모든 경우를 검사
int visited = que.front();
que.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < wn; i++) {
if (!(visited & (1 << i))) {//현재 위치가 검사되지 않았다면
int t = visited | (1<<i);//현재 위치 입력
int next = (i + 1) % wn;
int val = i < next ? weak[next] - weak[i] : n - weak[i] + weak[next];
while (val <= dist[depth] && !(t & (1<<next))) {
t |= (1 << next);
next = (next + 1) % wn;
val = i < next ? weak[next] - weak[i] : n - weak[i] + weak[next];
}
if (t == n_bit - 1)//모든 위치가 검사 되었다면 종료
return depth + 1;
if (visited != t)que.push(t);//추가로 검사한 위치가 있다면 푸쉬
}
}
}
++depth;
}
return -1;
}
|
cs |
2. 퍼뮤테이션
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int solution(int n, vector<int> weak, vector<int> dist) {
int wn = weak.size(), dn = dist.size();
sort(dist.begin(), dist.end());//퍼뮤테이션 조건 : 정렬
int answer = dn;//최대 depth 설정
for (int i = 0; i < wn; i++) {
weak.push_back(weak.front() + n);//외벽 위치 순환
weak.erase(weak.begin());
do {
int w_idx = 0, depth = 0;//w_idx : 현재 검사 위치, depth : 사람 수
while (depth < answer) {
int end = weak[w_idx] + dist[depth];//현재 위치에서 갈 수 있는 곳 까지 검사
while (w_idx != wn && end >= weak[w_idx])
++w_idx;
if (w_idx != wn)
++depth;
else break;
}
if (w_idx == wn) {//모든 위치를 검사하면
if (depth < answer) {
answer = depth;
}
}
} while (next_permutation(dist.begin(), dist.end()));
}
return answer < dn ? answer + 1 : -1;
}
int main() {
vector<int> w_idx = { 1, 5, 6, 10 };
vector<int> depth = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
cout << solution(100, w_idx, depth);
}
|
cs |
반응형
'알고리즘 문제 > [프로그래머스]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [프로그래머스] 가사 검색 (0) | 2021.03.18 |
|---|---|
| [프로그래머스] 블록 이동하기 (0) | 2021.03.18 |
| [프로그래머스] 기둥과 보 설치 (0) | 2021.03.14 |
| [프로그래머스] 자물쇠와 열쇠 (0) | 2021.03.11 |
| [프로그래머스] 괄호 변환 (0) | 2021.03.10 |